Are You Looking For a Physiotherapist In Adamstown, Newcastle - NSW?
Why Book at Sport & Spine Physiotherapy?
Expert Care. Proven Results. Convenient Location.
When it comes to your health, you deserve the best and that’s exactly what we deliver.
At Sport & Spine Physiotherapy, we combine clinical expertise with genuine care to provide results-driven physiotherapy that puts you first.
Our experienced team doesn’t just treat symptoms, we pride ourselves on our pain to performance approach to client care where we take the time to understand the root cause of your pain and create a personalised plan to help you move better, feel stronger and get back to what you love. Our model is relieving symptoms, restoring function and improving your long term health.
Because it's not just about living longer—it's about living well. Prioritising your health span means staying active and independent for as many years as possible.
Make your health a priority and book an appointment with one of our expert physios and take the first step towards better health.
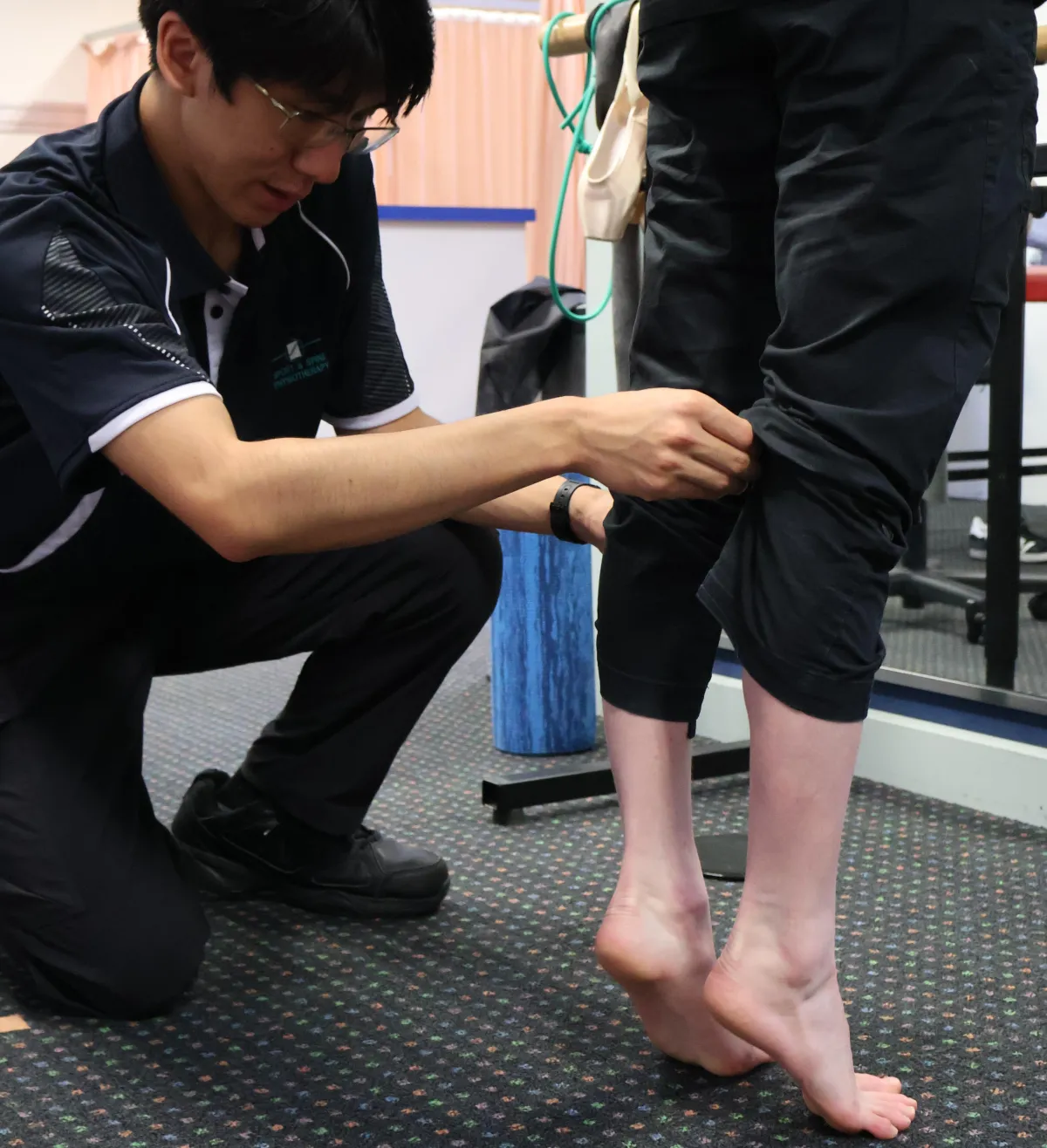
Sport & Spine Physiotherapy was established in 1993 and has consistently provided a high standard of Physiotherapy care to the people of Newcastle and the Hunter Valley
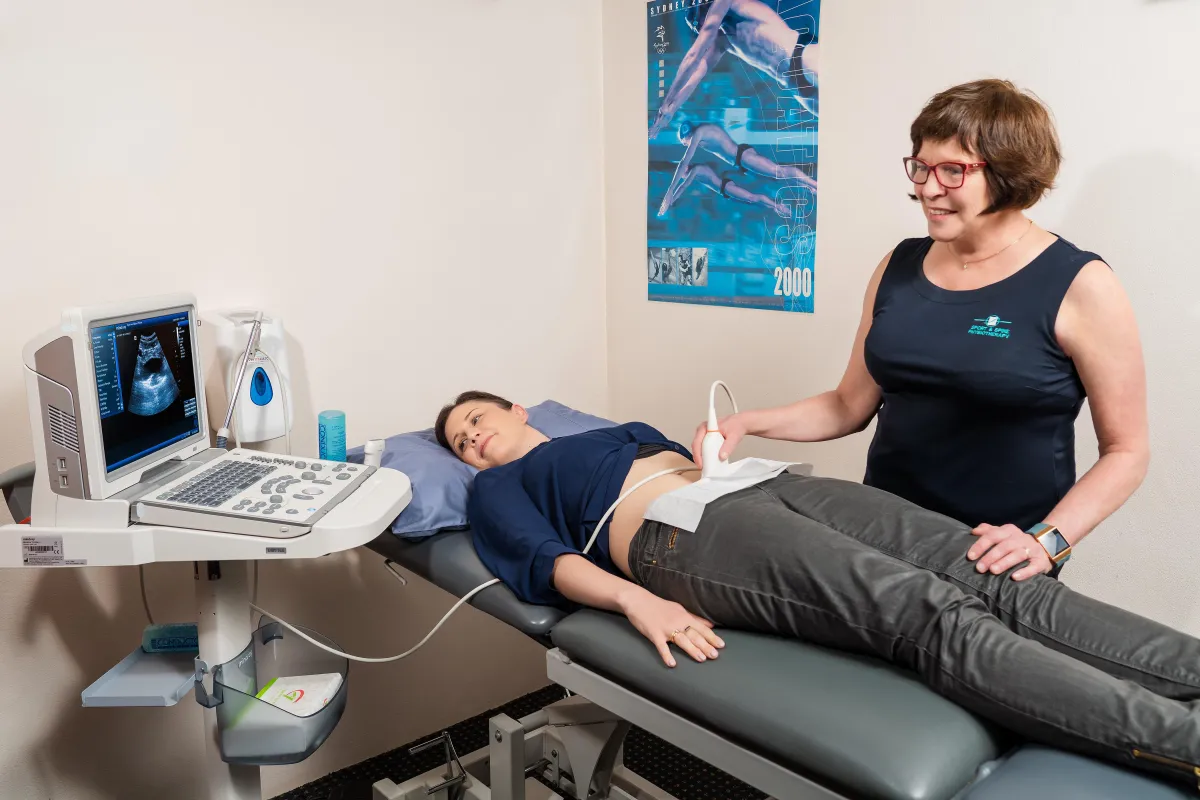
What Sets Us Apart?
We have been serving Newcastle and the Hunter Valley for over 40 years, we know our community and its needs.
With over 40 years of clinical experience our team brings a depth of knowledge that few clinics can match. We've seen almost every type of injury and condition—and we know what works.
We pride ourselves on our pain to performance approach to client care; relieving symptoms, restoring function and improving your long term health.
Confused about your pain and not sure what to do?
Get clear, professional advice in our free downloadable information packs
Back Pain
Understand why back pain happens and how to help it
Shoulder Pain
Understand why shoulder pain happens and how to help it
Knee Pain
Understand why knee pain happens and how to help it
How Can We Help?
At Sport & Spine Physiotherapy we treat a wide range of conditions from everyday aches to complex injuries. Whether you're dealing with a recent injury or something that’s been nagging you for a while, our experienced physiotherapists can help you understand the cause and work towards lasting relief.
We commonly help clients with:
Back pain – from stiffness and postural strain to disc injuries and sciatica
Neck pain & headaches – including tension, whiplash and desk-related strain
Shoulder pain – such as rotator cuff issues, bursitis and frozen shoulder
Knee pain – from ligament injuries and arthritis to patellofemoral pain
Hip & pelvic pain – affecting movement, stability or sleep
Ankle & foot problems – including sprains, Achilles issues and plantar fasciitis
Post-surgical recovery – regain strength and mobility after orthopaedic surgery
Sports injuries – from sprains and strains to overuse injuries
Balance and dizziness issues – including BPPV and vestibular dysfunction
Contact us today to speak with our friendly team and find out how we can help you feel your best
Latest Tips and Advice
Regain Strength and Mobility with Clinical Pilates for Shoulder Pain in Adamstown, Newcastle
Ease shoulder pain with Clinical Pilates at Sport & Spine Physiotherapy Adamstown. Physio-led programs to restore strength, control and mobility. ...more
Physiotherapy
November 06, 2025•3 min read
Move Better, Feel Stronger: Clinical Pilates for Back Pain in Adamstown, Newcastle
Relieve and prevent back pain with Clinical Pilates at Sport & Spine Physiotherapy Adamstown. Physio-guided programs for strength and spinal control. ...more
Physiotherapy
October 30, 2025•2 min read
Recover Stronger After Surgery with Clinical Pilates in Adamstown, Newcastle
Recover safely after surgery with Clinical Pilates at Sport & Spine Physiotherapy Adamstown. Tailored post-surgical rehab for strength, stability & control. ...more
Physiotherapy
October 23, 2025•2 min read
We’re proud to be connected with trusted professional affiliations and community partners





Sport & Spine Physiotherapy is powered by Vitala Health, a group of Allied Health Practices across New Zealand and Australia.
Vitala Health provides clinical solutions that supports clients health and lifestyle needs through best practice treatment, premium facilities, education and ongoing commitment to customer service. Learn more about Vitala Health
If you have any questions before scheduling an appointment or for general enquiries, please use the contact us. Our team will promptly reach out to assist you.
Opening Hours
Mon: 8:00am - 7:00pm
Tue: 11:00am - 7:00pm
Wed: 8:00am - 4:00pm
Thu: 8:00am - 7:00pm
Fri: 8:00am - 6:30pm
Sat: Closed
Sun: Closed


Follow Us
The Clinic
Common conditions
© Copyright 2025. Vitala Health. All rights reserved.

Facebook
Instagram